Помогите с решением задач
Problem 1. Find the Bugs (5 points each)
The following routines each have one bug. Correct each one.
a. This function is supposed to append string_tail to the end of string_head without using the strcat() function. It assumes that string_head has enough room to contain the result.
Problem 1. Find the Bugs
b. String Look-up
This function returns the look-up table string given a key. Passing the string “tofu” should return a pointer to “soy beans”. Passing the string “chickens” should return a NULL pointer.
Problem 1. Find the Bugs
c. This function accepts an MS-DOS pathname string, which is of the form
drive_letter:\directory\...\directory\filename.extension
It returns a pointer to the start of the base filename. For example, given the string “c:\source\graph\spin.c” it returns a pointer to the character “s” in “spin”.
Problem 1. Find the Bugs
d. This function initializes each element of an array to contain its own index.
Problem 2. High Quality Code (10 points each)
Rewrite the following code fragments to turn them into production-quality code. (Don’t forget that good code includes comments.)
a. Machine-Dependence and Non-Portability:
This function finds the centroid, or average, of two two-dimensional points A and B:
Problem 2. High Quality Code
b. Error Checking:
This function reads a string, preceded by a two-byte length, from a file into a C-style string in memory.
char *ReadStringFromFile(FILE *fp)
{
char *str;
int length;
fread(&length, 2, 1, fp);
str = malloc(length + 1);
fread(str, 1, length, fp);
str[length] = 0;
return str;
}
Problem 3. Linked-List enhancement (30 points)
Given the data structure item as an item in a linked list, write the function AddKey() to add a node to the list. Maintain the list sorted by key.
Include a comment describing how the function behaves, your assumptions, and the return value from the function. Be sure to think about special cases and possible errors
Problem 4. Loop Optimization (Bonus — 10 points. Do the other problems first.)
Rewrite the function for fast execution. Assume that the compiler makes no op¬timizations and generates code literally from the source. Do not use register variables.
The following routines each have one bug. Correct each one.
a. This function is supposed to append string_tail to the end of string_head without using the strcat() function. It assumes that string_head has enough room to contain the result.
Код:
char* AppendString(char* string_head, char* string_tail)
{
int length;
length = strlen(string_tail);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
{
int length;
length = strlen(string_tail);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
Problem 1. Find the Bugs
b. String Look-up
This function returns the look-up table string given a key. Passing the string “tofu” should return a pointer to “soy beans”. Passing the string “chickens” should return a NULL pointer.
Код:
static char* arrayLookup[] =
{
"eggs", "chickens",
"tofu", "soy beans",
"coriander", "cilantro",
"yeast", "wheat"
};
char* LookupString(char* string_key)
{
char** strIndex;
for (strIndex = arrayLookup; strIndex; strIndex += 2)
{
if (!strcmp(*strIndex, string_key))
{
return strIndex[1];
}
}
return NULL;
}
{
"eggs", "chickens",
"tofu", "soy beans",
"coriander", "cilantro",
"yeast", "wheat"
};
char* LookupString(char* string_key)
{
char** strIndex;
for (strIndex = arrayLookup; strIndex; strIndex += 2)
{
if (!strcmp(*strIndex, string_key))
{
return strIndex[1];
}
}
return NULL;
}
Problem 1. Find the Bugs
c. This function accepts an MS-DOS pathname string, which is of the form
drive_letter:\directory\...\directory\filename.extension
It returns a pointer to the start of the base filename. For example, given the string “c:\source\graph\spin.c” it returns a pointer to the character “s” in “spin”.
Код:
char* FindBasename(char* string_filename)
{
int i;
/* Look for the beginning of the filename: */
for (i = strlen(string_filename); i; i--)
{
switch (string_filename[i - 1])
{
case ':': /* Look for path separators */
case '\\':
break; /* Quit when one is found */
}
}
/* Return a pointer to the filename: */
return string_filename + i;
}
{
int i;
/* Look for the beginning of the filename: */
for (i = strlen(string_filename); i; i--)
{
switch (string_filename[i - 1])
{
case ':': /* Look for path separators */
case '\\':
break; /* Quit when one is found */
}
}
/* Return a pointer to the filename: */
return string_filename + i;
}
Problem 1. Find the Bugs
d. This function initializes each element of an array to contain its own index.
Код:
void InitArray(int* array, int array_length)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < array_length)
{
array[i] = i++;
}
}
{
int i = 0;
while (i < array_length)
{
array[i] = i++;
}
}
Problem 2. High Quality Code (10 points each)
Rewrite the following code fragments to turn them into production-quality code. (Don’t forget that good code includes comments.)
a. Machine-Dependence and Non-Portability:
This function finds the centroid, or average, of two two-dimensional points A and B:
Код:
long Centroid(long A, long B)
{
int x, y;
x = ((int) (A >> 16) + (int) (B >> 16)) / 2;
y = ((int) A + (int) B) / 2;
return ((long) x << 16) + y;
}
{
int x, y;
x = ((int) (A >> 16) + (int) (B >> 16)) / 2;
y = ((int) A + (int) B) / 2;
return ((long) x << 16) + y;
}
b. Error Checking:
This function reads a string, preceded by a two-byte length, from a file into a C-style string in memory.
char *ReadStringFromFile(FILE *fp)
{
char *str;
int length;
fread(&length, 2, 1, fp);
str = malloc(length + 1);
fread(str, 1, length, fp);
str[length] = 0;
return str;
}
Problem 3. Linked-List enhancement (30 points)
Given the data structure item as an item in a linked list, write the function AddKey() to add a node to the list. Maintain the list sorted by key.
Include a comment describing how the function behaves, your assumptions, and the return value from the function. Be sure to think about special cases and possible errors
Код:
typedef struct _NODE
{
struct _NODE *node_next;
int key;
char *data;
} ITEM, *NODE, *LIST;
LIST AddKey (LIST list, int key, char* data);
{
struct _NODE *node_next;
int key;
char *data;
} ITEM, *NODE, *LIST;
LIST AddKey (LIST list, int key, char* data);
Problem 4. Loop Optimization (Bonus — 10 points. Do the other problems first.)
Rewrite the function for fast execution. Assume that the compiler makes no op¬timizations and generates code literally from the source. Do not use register variables.
Код:
char* SlowFunction(char* output, char* input)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; input[i]; ++i)
{
if (input[i] >= ' ' && input[i] < 'a')
{
output[j++] = input[i];
}
if (input[i] >= 'a' && input[i] <= 'z')
{
output[j++] = input[i] - ('a' - 'A');
}
if (input[i] > 'z' && input[i] < 0x7f)
{
output[j++] = input[i];
}
}
output[j] = '\0';
return output;
}
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; input[i]; ++i)
{
if (input[i] >= ' ' && input[i] < 'a')
{
output[j++] = input[i];
}
if (input[i] >= 'a' && input[i] <= 'z')
{
output[j++] = input[i] - ('a' - 'A');
}
if (input[i] > 'z' && input[i] < 0x7f)
{
output[j++] = input[i];
}
}
output[j] = '\0';
return output;
}
Я, например, не вижу никакого бага в первом задании, тем более что предполагается, что string_head имеет достаточно места для получения результата... Главное чтобы размер массива под строку string_head был достаточен, чтобы включить размер массива под строку string_tail, а чтобы осуществить проверку, то это уже не баг, а проблема реализации самой функции...
Например в этом случае выполнится без проблем:
а в данном случае не выполнится:
Например в этом случае выполнится без проблем:
Код:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char* AppendString (char* string_head, char* string_tail);
void main(){
char string_head[9] = "dddd";
char string_tail[5] = "hhhh";
cout << AppendString(string_head, string_tail);
//return;
}
char* AppendString(char* string_head, char* string_tail)
{
int length;
length = strlen(string_tail);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
using namespace std;
char* AppendString (char* string_head, char* string_tail);
void main(){
char string_head[9] = "dddd";
char string_tail[5] = "hhhh";
cout << AppendString(string_head, string_tail);
//return;
}
char* AppendString(char* string_head, char* string_tail)
{
int length;
length = strlen(string_tail);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
Код:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char* AppendString (char* string_head, char* string_tail);
void main(){
char string_head[8] = "dddd";
char string_tail[5] = "hhhh";
cout << AppendString(string_head, string_tail);
//return;
}
char* AppendString(char* string_head, char* string_tail)
{
int length;
length = strlen(string_tail);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
using namespace std;
char* AppendString (char* string_head, char* string_tail);
void main(){
char string_head[8] = "dddd";
char string_tail[5] = "hhhh";
cout << AppendString(string_head, string_tail);
//return;
}
char* AppendString(char* string_head, char* string_tail)
{
int length;
length = strlen(string_tail);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
Цитата: Алексей Иевенко
Я, например, не вижу никакого бага в первом задании
Я бы не был столь категоричен. Эти функции работают с ASCIIZ-строками, и если в конце не будет нуля, то программа имеет все шансы упасть, а это баг.
Да там-же очевидно надо length = strlen(string_head);
А насчет нультерминированности надо в доках писать. Прототип ничего сказать не может.
А насчет нультерминированности надо в доках писать. Прототип ничего сказать не может.
Код:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
//Соединение двух c-строк (нультерминир.)
//string_head должна быть достаточной для хранения результата
char* AppendString(char* string_head, char* string_tail) {
int length;
length = strlen(string_head);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
int main() {
char a[1024] = "abcdef";
std::cout << AppendString(a,"GHJK") << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#include <cstring>
//Соединение двух c-строк (нультерминир.)
//string_head должна быть достаточной для хранения результата
char* AppendString(char* string_head, char* string_tail) {
int length;
length = strlen(string_head);
strcpy(string_head + length, string_tail);
return string_head;
}
int main() {
char a[1024] = "abcdef";
std::cout << AppendString(a,"GHJK") << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Цитата: @pixo $oft
Цитата: Алексей Иевенко
Я, например, не вижу никакого бага в первом задании
Я бы не был столь категоричен. Эти функции работают с ASCIIZ-строками, и если в конце не будет нуля, то программа имеет все шансы упасть, а это баг.
Не стараюсь быть категоричным... Но ведь не проблема самих функций, что строки могут быть переданы не нультерминированные.... Вы же сами говорите, что: "если в конце не будет нуля...", а это проблема больше реализации, чем баг ... Что мешает проверить входящие строки на присутствие '\0'...?
Дело в эффективности. С, например, по этой причине не проверяет границ массивов. Если нужна надежность, вводите проверки. Все на откуп программиста. Главноое при использовании "эффективных" решений -- четкая документированность.
Цитата: sadovoya
Дело в эффективности. С, например, по этой причине не проверяет границ массивов. Если нужна надежность, вводите проверки. Все на откуп программиста. Главноое при использовании "эффективных" решений -- четкая документированность.
Именно... дело программиста осуществлять проверки... и принимать наиболее эффективные решения...
Problem1 c) Решается так (выход return, а не break):
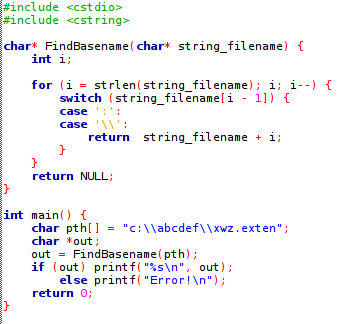
Хотя в MS-DOS имена в формате 8+3, но здесь не принципиально.
P.S. Когда наконец исправят всавку обратных слешей? Приходится уже код картинками вставлять.

Хотя в MS-DOS имена в формате 8+3, но здесь не принципиально.
P.S. Когда наконец исправят всавку обратных слешей? Приходится уже код картинками вставлять.
Цитата: sadovoya
Когда наконец исправят всавку обратных слешей? Приходится уже код картинками вставлять.
экранируй их обратным слэшем: \\n
Не вариант. Когда исправят вставку слешей, появятся лишние.
Loop Optimization
Problem 2 a.
В примере хранят в одном long две координаты точки. При этом исходят из того, что long 32 бита и int - 16. Переделать лучше через структуры с хранением пар координат, поменяв прототип. Без изменения прототипа сложней. Вот заготовка решения:
С нечетностью бит в long можно попробовать разобраться такой заменой:
И требованием к пользователям в long учитывать только не усекаемые таким представлением биты (на их платформах).
В примере хранят в одном long две координаты точки. При этом исходят из того, что long 32 бита и int - 16. Переделать лучше через структуры с хранением пар координат, поменяв прототип. Без изменения прототипа сложней. Вот заготовка решения:
Код:
//===========================================================
//Заготовка решения с сохранением прототипа ф-ции из задания.
//~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//
//Ограничения:
//------------
// 1)long должен быть из четного колич. бит;
// 2)координаты не отрицательные.
//===========================================================
#include <cstdio>
#include <climits> //для CHAR_BIT
#define NEW_LINE char(10)
//Координаты задавать в половинках long.
long Centroid(long A, long B) {
static const unsigned half_long_bits = sizeof(long)*CHAR_BIT/2;
union akaLong
{
struct
{
long field_a: half_long_bits;
long field_b: half_long_bits;
};
long both_fields;
} AA, BB, CC;
AA.both_fields = A;
BB.both_fields = B;
//тут бы еще проверку на переполнение
CC.field_a = (AA.field_a + BB.field_a)/2;
CC.field_b = (AA.field_b + BB.field_b)/2;
return CC.both_fields;
}
int main() {
//Пример использования для 32-битного long
printf("%#lX%c", Centroid(0x00010002, 0x00030004), NEW_LINE);
return 0;
}
//Заготовка решения с сохранением прототипа ф-ции из задания.
//~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//
//Ограничения:
//------------
// 1)long должен быть из четного колич. бит;
// 2)координаты не отрицательные.
//===========================================================
#include <cstdio>
#include <climits> //для CHAR_BIT
#define NEW_LINE char(10)
//Координаты задавать в половинках long.
long Centroid(long A, long B) {
static const unsigned half_long_bits = sizeof(long)*CHAR_BIT/2;
union akaLong
{
struct
{
long field_a: half_long_bits;
long field_b: half_long_bits;
};
long both_fields;
} AA, BB, CC;
AA.both_fields = A;
BB.both_fields = B;
//тут бы еще проверку на переполнение
CC.field_a = (AA.field_a + BB.field_a)/2;
CC.field_b = (AA.field_b + BB.field_b)/2;
return CC.both_fields;
}
int main() {
//Пример использования для 32-битного long
printf("%#lX%c", Centroid(0x00010002, 0x00030004), NEW_LINE);
return 0;
}
Код:
static const size_t half_bits = sizeof(long)*CHAR_BIT/2;
static const size_t bits = half_bits*2;
union akaLong
{
struct
{
long field_a: half_bits;
long field_b: half_bits;
};
long both_fields: bits;
} AA, BB, CC;
static const size_t bits = half_bits*2;
union akaLong
{
struct
{
long field_a: half_bits;
long field_b: half_bits;
};
long both_fields: bits;
} AA, BB, CC;
И требованием к пользователям в long учитывать только не усекаемые таким представлением биты (на их платформах).

